You can use ChatGPT for content creation, but what about development tasks such as coding, security, web, and debugging?
We will not say the 5th version has exceptional capabilities that can match a professional developer’s expectations. Nothing compared to Github Copilot or Sonet 3.5.
- Why Do Developers Need to Engineer Prompts?
- 5 Tools & Frameworks for Prompt Engineering
- 7 Real-Life Use Cases of Prompt Engineering for Developers
- 15 Best ChatGPT Prompt Examples for Developers
- FAQs on ChatGPT Prompt Engineering for Developers
- In 2025, ChatGPT Prompt Engineering for Developers is just a Basic Concept
However, using it correctly can help you utilize this chatbot in some cases perfectly such as debugging, testing, and deployment. So, how does ChatGPT prompt engineering for developers work?
Let’s deep dive further!
Why Do Developers Need to Engineer Prompts?
In 2025, prompt engineering is becoming really important for you as a developer, especially when using AI tools like ChatGPT. While AI can help with tasks like app development, algorithms, and cybersecurity, it still needs your guidance to give the best results.
By writing clear prompts, you can make sure the AI gives you accurate and helpful answers, saving you time on things like debugging or improving your code.
For example, when working on an ethical hacking project, well-crafted prompts will help the AI come up with attack scenarios based on specific weaknesses. Besides practical reasons, you may require prompt engineering for –
i. Accurate Responses that Match Your Intent
When you master prompt engineering, you can get accurate responses that match your intent. By crafting clear and specific prompts, you guide the AI to understand the context and provide solutions that are more aligned with what you need.
This reduces the chances of getting irrelevant or vague answers, ensuring that the AI’s output is tailored to your requirements.
ii. Faster Results with Less Trial and Error
With prompt engineering, you can achieve faster results with less trial and error. By refining your prompts, you teach the AI exactly what you’re looking for, minimizing the need to try multiple variations or rework the generated content.
This allows you to move through tasks quickly, saving you time that would otherwise be spent revising or re-asking for corrections.
iii. Better Control Over Tone and Format
You also gain better control over tone and format when working with AI. Whether you need technical documentation, casual dialogue, or code snippets, prompt engineering helps you direct the AI to produce content in the tone and structure that suits your project.
Giving details to your input, lets you control the results of your output. Maintain consistency and clarity across your work to avoid the need for heavy post-editing.
iv. Smarter Problem-Solving Through Structure
Through well-structured prompts, smarter problem-solving becomes possible. By providing the AI with clear instructions on how to approach a problem or break down a task, you can guide it to focus on the most relevant aspects, leading to more effective solutions.
Whether troubleshooting an issue or creating a new feature, structure helps the AI generate step-by-step guidance that’s easier to follow and apply. You can also use tha ChatGPT Agent mode for better task automation and structuring for your programming part.
v. Advanced Use Cases Unlocked with Precision
Lastly, advanced use cases are unlocked when you can precisely craft prompts. With the right level of detail, you can use AI for more complex tasks like creating security algorithms, running simulations, or even generating business-specific solutions.

By mastering prompt engineering, you gain the ability to explore new, higher-level use cases that can drive innovation and efficiency in your work.
5 Tools & Frameworks for Prompt Engineering
In 2025, you can have access to powerful tools and frameworks that make prompting more structured, efficient, and reliable.
1. Claude
Right now, learning Claude isn’t optional it’s survival.
Claude has become the developer’s most powerful co-pilot, capable of reading entire repositories and refactoring legacy systems with ease. It also generates precise documentation and reasons through logic flaws better than most human peers.

Claude doesn’t just automate coding, it amplifies creativity, speed, and clarity. Companies now expect developers to deliver AI-assisted output. Claude’s massive context, accuracy, and safe reasoning make it the top choice for enterprises.
Whether you’re junior or senior, mastering Claude means writing, reviewing, and shipping smarter. Ignoring it risks falling behind as AI-native developers redefine productivity, collaboration, and technical excellence across every modern software team.
2. ChatGPT Playground
The ChatGPT Playground is a user-friendly platform where you can experiment with different prompts and settings for OpenAI’s language models. You can customize the temperature, response length, and other settings to see how the model responds to different inputs.
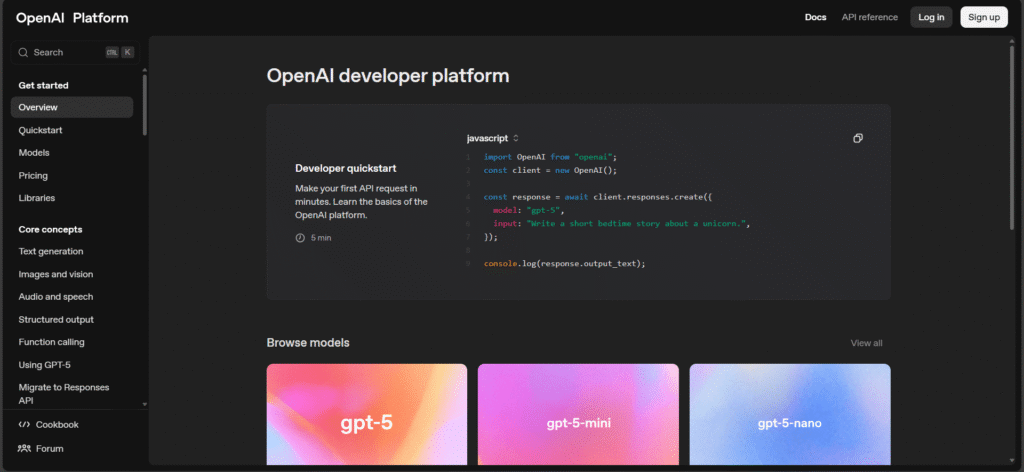
By using the Playground, you can experiment with different settings to see how they affect the quality and tone of the responses.
It’s a great way to get a feel for how ChatGPT processes prompts and helps you refine your queries to get the best results for what you need.
3. Notion
Notion is an all-in-one workspace that allows you to organize notes, documents, tasks, and databases. This prompt engineering tool can help you create structured templates for your ideas, streamlining your workflow and making it easier to organize your projects.

Notion’s ability to collaborate in real time also makes it ideal for teams. That’s not all, Notion can,
- Organize notes, tasks, and projects all in one space.
- Access pre-built templates for faster workflows.
- Store data in customizable tables, boards, or lists.
- Generate content and ideas with the AI assistant built into Notion.
- Personalize your workspace layout to fit your needs.
4. Google Apps with Gemini
Google Sheets with AI add-ons is a powerful tool for prompt engineers who need to scale their work. By integrating AI-powered add-ons like Gemini, you can automatically generate or optimize prompts directly within your Sheets, Docs, Slides, Gmail, and Drive.
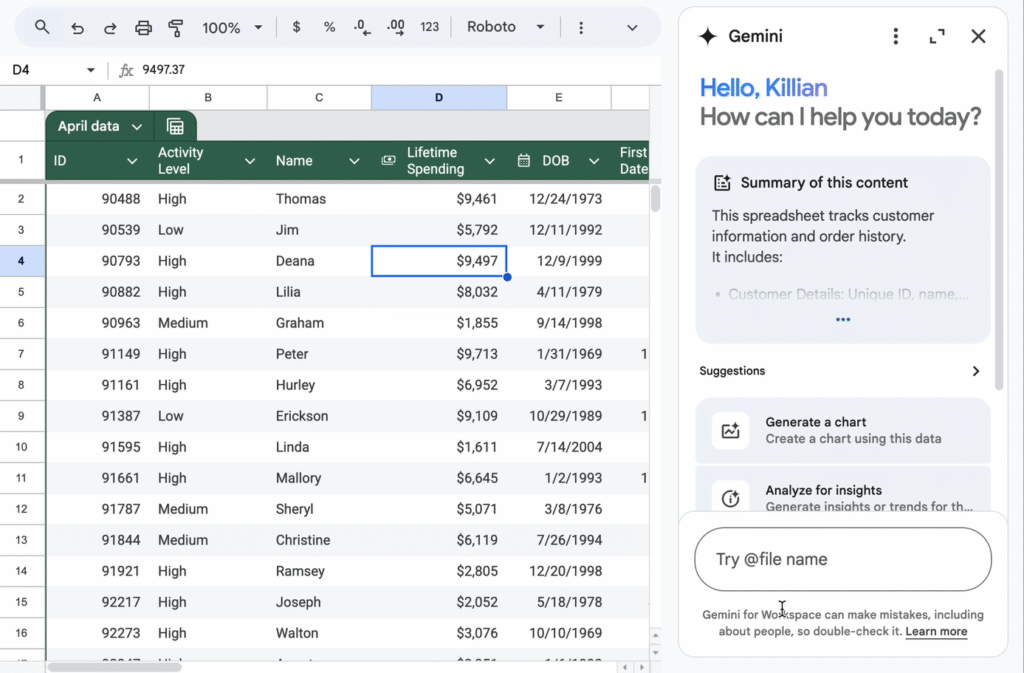
But you have to buy the Google One subscription for the Gemini Icon to appear on your tools.
5. GitHub Copilot
GitHub Copilot works as your coding assistant directly inside the editor. You can write natural prompts, and it suggests code snippets, functions, or even full modules. This makes your development process faster and more efficient.
With prompt engineering, you can guide Copilot to match your coding style and project needs. You can rely on it for debugging, writing unit tests, or exploring new frameworks.
Over time, it helps you improve productivity while keeping your focus on problem-solving.
6. Anthropic’s Prompt Generator tool
Using the Anthropic Console Prompt Generator, you can fine-tune your prompts to get the most relevant and accurate responses from Claude AI. You can
For example, if you want Claude to generate a detailed explanation of a technical concept, you can specify the level of depth and clarity you require, such as requesting a simple overview or a step-by-step guide.
If you’re working on creative tasks, the console allows you to direct Claude to produce content in a specific style, tone, or voice, ensuring it aligns with your project requirements.
7 Real-Life Use Cases of Prompt Engineering for Developers
So, in which areas of development can you use prompt engineering? Let’s find out.
1. Code Generation & Debugging
Prompt engineering enables you to generate code snippets that are customized to your specific requirements. ChatGPT can suggest efficient algorithms and help streamline your development process by providing accurate code examples.
When debugging, AI models can assist in pinpointing issues and offer targeted recommendations for fixing errors.
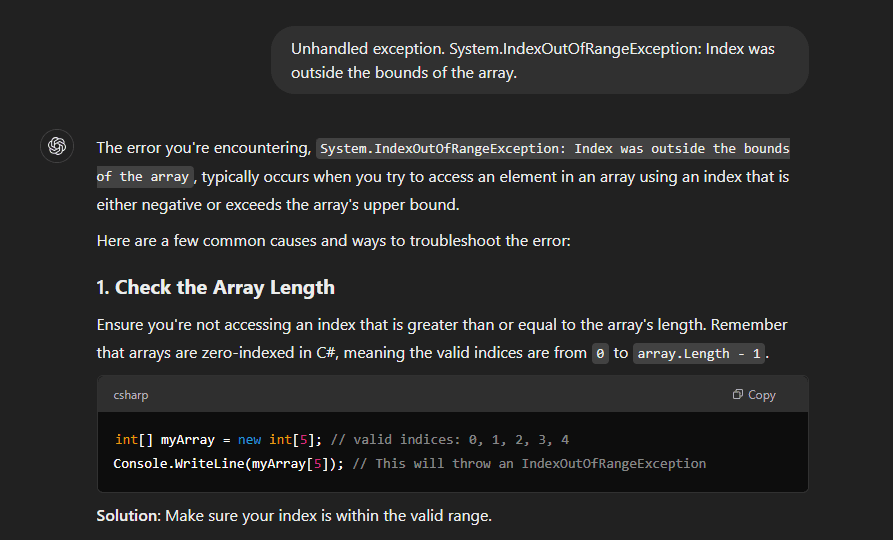
With the ability to identify common coding pitfalls, the model can provide solutions that accelerate the troubleshooting process.
2. API Design & Documentation
You can leverage prompt engineering to structure and design your API efficiently, ensuring the endpoints align with your application’s needs. AI can help clarify complex API functionalities, making it easier for your team to understand and implement.
AI can automatically generate comprehensive documentation, including sample requests and responses for each API endpoint.
This allows developers to quickly grasp the API structure and reduces the overhead of manual documentation.
3. Automated Testing with AI-generated Cases
Prompt engineering helps you build detailed test cases faster. You can specify scenarios, and the AI will generate test inputs and expected outputs. This saves you time by covering both common and edge cases. You get stronger testing coverage without writing every test manually.
You can focus on logic while the AI covers repetitive tasks. This makes your software or web page more reliable from the start.
4. Data Analysis & Visualization Prompts
You can use prompts to explore datasets in a more interactive way. By asking the AI to analyze data, you get summaries, trends, and patterns explained clearly. Visualization prompts help turn complex data into charts, tables, and graphs.
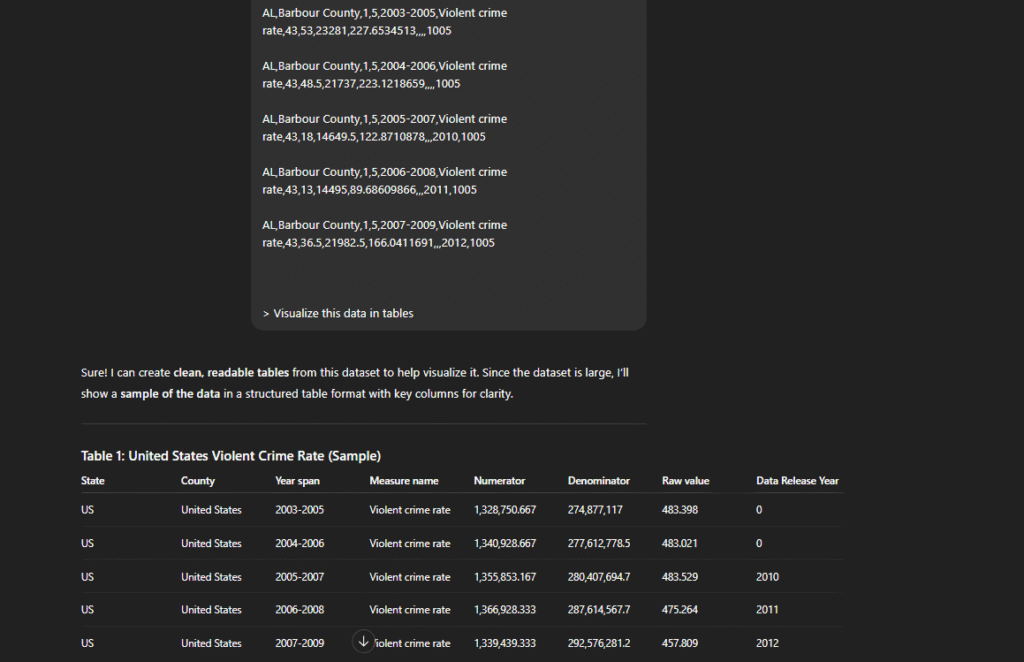
You spend less time setting up visuals manually. The AI helps you spot important findings much faster.
Also, you can copy the simple data using the button located here,
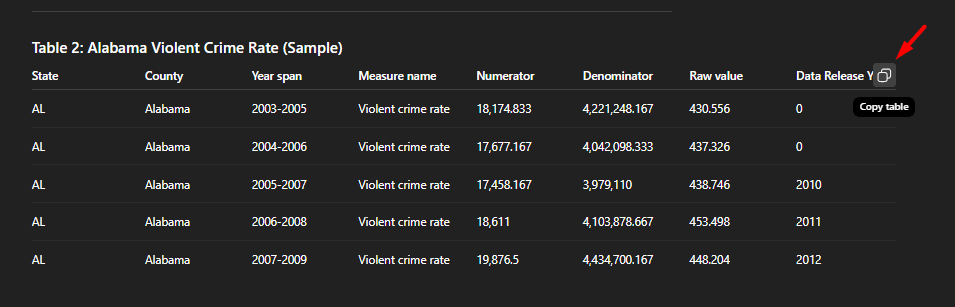
5. Writing Technical Content (REDMEs, Guides)
You will need to write technical documentations such as READMES, Guides, and Terms & Conditions.
With prompt engineering, you can draft technical content quickly. By stating the purpose, structure, and audience, the AI generates well-organized material. This is useful for writing README files or step-by-step guides, ensuring your documentation is easy to read and follow.

You can modify the output further to adjust it as many times as you want. Remember to take screenshots, while I did in this article.
6. Building Chatbots and Virtual Assistants for Apps
You can use prompt engineering to design smarter chatbots. By crafting prompts with context, you teach the AI how to answer user questions naturally.
This improves the chatbot’s ability to handle real conversations. It also makes virtual assistants more helpful inside your apps, guiding AI to use a friendly or professional tone.
In a typical question-based (based on the app or website it’s positioned) chatbot, you can except,
- Accurate and context-aware answers to user questions.
- Responses that match the tone you’ve specified, whether friendly or professional.
- Faster handling of repeated or common queries without human intervention.
- Step-by-step guidance or suggestions when users ask complex questions.
- Continuous learning from previous interactions to improve future responses.
7. Optimizing Database Queries
Prompt engineering helps you write efficient database queries. You can describe the data you want, and the AI suggests optimized SQL commands. This reduces execution time and improves performance.
It also ensures your queries are easier to maintain and scale. You avoid writing slow or redundant code. Over time, this leads to smoother data operations in your projects.
15 Best ChatGPT Prompt Examples for Developers
We’ve covered the tools and fields of prompt engineering, now let’s look at some great prompt examples for developers.
1. Code Generation
I need to implement [specific functionality] in [programming language].
Key requirements:
> [Requirement 1]
> [Requirement 2]
> [Requirement 3]
Please consider:
> Error handling
> Edge cases
> Performance optimization
> Best practices for [language/framework]
> Please do not unnecessarily remove any comments or code.
> Generate the code with clear comments explaining the logic.
2. Code Explanation
Can you explain the following part of the code in detail:
[paste code section]
Specifically:
> What is the purpose of this section?
> How does it work step-by-step?
> Are there any potential issues or limitations with this approach?
3. Code Review
Please review the following code:
[paste your code]
Consider:
> Code quality and adherence to best practices.
> Potential bugs or edge cases.
> Performance optimizations.
> Readability and maintainability.
> Any security concerns.
> Suggest improvements and explain your reasoning for each suggestion.
4. Algorithm Implementation
Implement a [name of algorithm] in [programming language].
Please include:
> The main function with clear parameters and return types.
> Helper functions if necessary.
> Time and space complexity analysis.
> Example usage.
5. Module Creation
Create a [class/module] for [specific functionality] in [programming language].
Include:
> Constructor/initialization.
> Main methods with clear docstrings.
> Any necessary private helper methods.
> Proper encapsulation and adherence to OOP principles.
6. Code Optimization
Here's a piece of code that needs optimization:
[paste code]
> Please suggest optimizations to improve its performance. For each suggestion, explain the expected improvement and any trade-offs.
7. Code Optimization
Generate unit tests for the following function:
[paste function]
Include tests for:
> Normal expected inputs.
> Edge cases.
> Invalid inputs.
> Use [preferred testing framework] syntax.
8. Bug Fixing
I’m encountering a bug in my code:
[paste code or error logs]
Please:
> Identify the root cause of the issue.
> Suggest fixes step by step.
> Provide an updated version of the code.
> Explain how to avoid this issue in the future.
9. Refactor Code
Here’s a piece of code that works but is messy:
[paste code]
Please refactor it to improve:
> Readability and maintainability.
> Use of best practices for [language/framework].
> Modularity and reusability.
> Explain the changes you made and why they help.
10. Documentation Writing
Please generate documentation for the following function or module:
[paste code]
Include:
> Clear description of purpose.
> Parameter details.
> Return values.
> Example usage.
> Make it concise but professional.
11. System Design
Design a system for [specific functionality] that should handle:
> Scalability for [number of users/requests]
> Data storage and retrieval
> Security and authentication
> Fault tolerance
> Provide diagrams in text format (like ASCII or structured lists) and explain your design decisions.
12. API Blueprint
I need to design an API for [specific purpose]:
Please provide:
> End point list with request/response formats
> Authentication method
> Example usage in [preferred language]
> Error handling approach
13. DevOps Setup
Generate a CI/CD pipeline configuration for [tool, e.g., GitHub Actions, Jenkins]:
Requirements:
> Build and test steps for [language/framework]
> Deployment to [environment]
> Error notifications
> Best practices for caching and speed optimization
14. Data Cleaning
I have a dataset in [CSV/JSON/SQL] format. Here’s a sample:
[paste data]
Please generate code in [preferred language] to:
> Remove duplicates.
> Handle missing values.
> Normalize column names
> Provide a summary report of cleaned data
15. Security Audit
Please audit the following code for security issues:
[paste code]
Check for:
> SQL injection risks.
> Cross-site scripting vulnerabilities.
> Unsafe data handling.
> Hardcoded secrets or keys.
> Suggest fixes for each vulnerability found.
FAQs on ChatGPT Prompt Engineering for Developers
In 2025, ChatGPT Prompt Engineering for Developers is just a Basic Concept
ChatGPT Prompt Engineering for Developers is just a basic concept. But let’s face it, most developers already have a solid grasp of it.
However, this isn’t the end of the story. As AI continues to evolve, prompt engineering will become even more critical. It’s no longer about simply giving commands to AI, it’s about strategically crafting prompts that extract the highest quality responses.
This skill will not only improve your productivity but will also give you a competitive edge in the tech world.
Mastering prompt engineering will transform how you interact with AI, making you a more efficient developer.

Loved it